Ever felt like your lessons or training sessions lack direction? You’re not alone. Whether in a classroom, boardroom, or workshop, unstructured learning often leads to confusion, missed goals, and disengaged participants. That’s where KWL charts come in—a simple yet powerful tool that turns scattered thoughts into purposeful learning.
KWL Chart Meaning
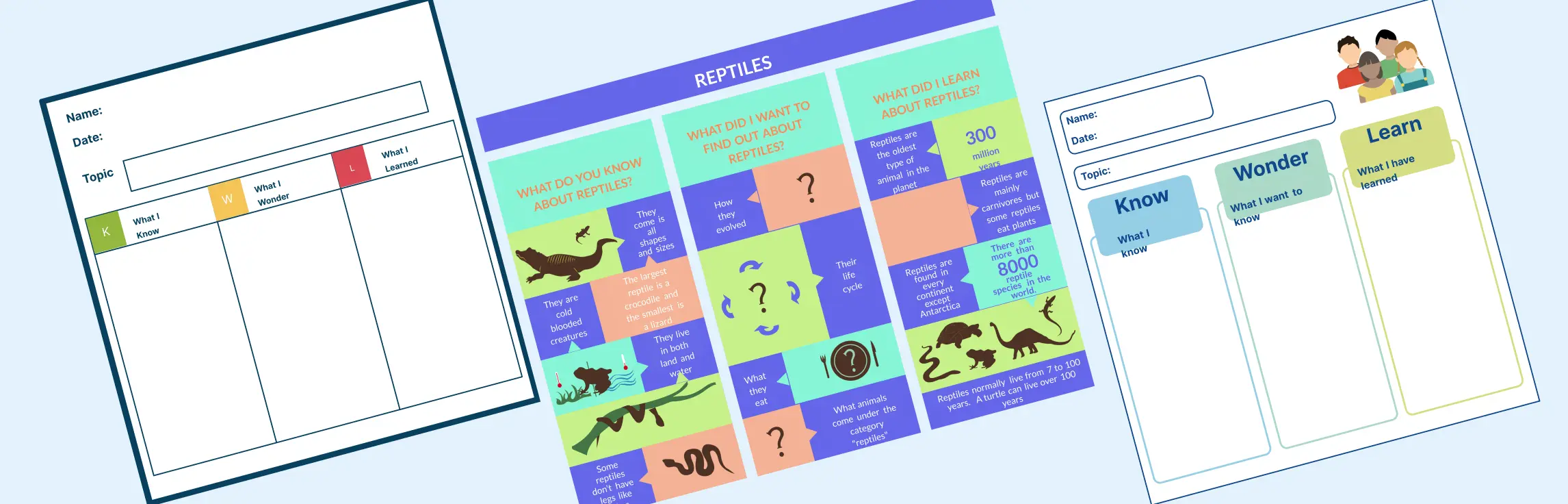
A KWL chart is a simple yet powerful tool for organizing learning. Short for “Know, Want to Know, and Learned,” this three-column graphic organizer is widely used in education and training to activate prior knowledge, set learning goals, and track progress.
Originally developed by Donna Ogle in 1986, the KWL chart supports active engagement with new information by tapping into existing knowledge and encouraging curiosity. It’s grounded in schema theory, which suggests learning is more effective when it connects to prior understanding.
Beyond K-12 classrooms, adult education programs and corporate workshops also leverage KWL charts to align training objectives with participant expectations. Workshop facilitators introduce the framework at the outset to surface existing expertise and tailor content in real time.
What Is a KWL Chart Used for?
The main purpose of a KWL chart is to transform passive learning into active inquiry. It’s used before, during, and after learning to support comprehension and reflection.
| Elements of a KWL Chart | ||
| Column | Purpose | Example Entry |
| Know | Activate prior understanding | “I know photosynthesis converts light into it energy.” |
| Want | Identify learning questions | “How do plants store energy?” |
| Learned | Reflect on new insights | “Chloroplasts store sugars as starch.” |
This structure gives both learners and instructors a clear path from baseline knowledge to measurable outcomes.
How KWL Charts Impact Learning
Integrating the KWL strategy into lessons or training programs enhances learning in several key ways:
- Makes content relevant and engaging by connecting it to what learners already know
- Promotes deeper understanding and longer-term retention of new concepts
- Encourages active thinking as learners generate their own questions and learning goals
- Supports the construction of meaning by linking prior knowledge with newly acquired information
- Builds learner confidence by recognizing and validating what they bring to the table
- Fosters ownership and accountability by turning learners into active participants in their own learning journey
By encouraging learners to reflect, question, and track their learning progress, the KWL chart serves as more than just a note-taking tool—it becomes a catalyst for meaningful, student-centered learning.
Benefits of Using KWL Charts
Using a KWL chart offers multiple benefits that make it a must-have for any learning environment. Here’s how it improves learning outcomes:
- Identifies knowledge gaps
- Promotes curiosity and motivation
- Enhances critical thinking
- Supports collaboration
- Tracks learning progress
- Improves retention
Read more: Top 7 KWL Chart Benefits for Classroom Learning
Real-World Examples of KWL Charts in Action with Templates
1. Classroom KWL Chart for History Lesson on Ancient Egypt
- Know: “Egyptians built pyramids.”
- Want: “Why were pyramids important?”
- Learned: “They were tombs for pharaohs and symbols of power.”
2. Reading Comprehension KWL Chart for Literature Class
- Know: “The story is set during a war.”
- Want: “How does war affect the main character?”
- Learned: “He loses family and gains empathy.”
3. Corporate Training KWL Chart for Employee Onboarding
- Know: “I’ve used HubSpot before.”
- Want: “How do I log new client tickets?”
- Learned: “Use the dashboard shortcut to add client issues.”
4. Workshop KWL Chart for Team Productivity Seminar
- Know: “We struggle with deadlines.”
- Want: “How can we prioritize better?”
- Learned: “Use the Eisenhower Matrix during sprint planning.”
These examples show the versatility of KWL charts across both academic and professional environments.
Explore: How to Make a KWL Chart
Digital KWL Charts: Enhancing Learning with Creately
Paper charts work, but digital KWL charts offer unmatched flexibility, especially for hybrid and remote learning.
Why Use Creately for KWL Charts?
Creately’s Online KWL Chart simplifies setup and maximizes collaboration.
Features That Enhance KWL Learning:
- Real-time editing for in-person or remote groups
- Customizable templates with drag-and-drop features
- Attach resources (slides, links, PDFs) to chart entries
- Exportable formats: PDF, PNG, or CSV
- Analytics to track engagement and learning progress
- Document management for archiving and version history
Whether you’re conducting a classroom lesson, onboarding workshop, or virtual seminar, Creately helps you turn basic KWL activities into interactive, visual learning experiences.
Conclusion: Empower Learners with KWL Charts
So, what is a KWL chart? It’s more than just a worksheet—it’s a learning framework that empowers individuals to take charge of their knowledge journey.
From classrooms to boardrooms, the KWL model improves engagement, curiosity, and retention. With tools like Creately, this classic method becomes even more powerful—combining visual thinking, collaboration, and real-time insights.
FAQs About KWL Charts
How do I create and use a KWL Chart?
Can KWL Charts Be Used for Group Activities?
Can I customize my own KWL Chart?
What questions should students ask in the W column of a KWL Chart?
What Is the Difference Between a KWL and KWHL Chart?
A KWL chart includes three columns:
- K – What I Know
- W – What I Want to know
- L – What I Learned
A KWHL chart adds a fourth column:
- H – How I will find the information
The H column encourages learners to think critically about their research methods and learning strategies. While the KWL chart focuses on knowledge and reflection, the KWHL chart adds an element of planning and metacognition, making it ideal for project-based learning, inquiry-based instruction, and independent study. In short, use a KWL chart for guided learning and a KWHL chart when you want to promote research skills and learning autonomy.