Ever faced a room full of blank stares before starting a new topic? The KWL reading strategy turns that uncertainty into curiosity. By helping learners tap into what they already know, define what they want to learn, and reflect on what they’ve discovered, this simple three-column method transforms reading into a focused, purpose-driven experience.
Whether you’re guiding a classroom, facilitating a workshop, or working one-on-one, the KWL method provides a flexible, repeatable framework to boost engagement and comprehension at every level.
What Is the KWL Reading Strategy?
KWL stands for:
- Know – What do I already know?
- Want to Know – What do I want to learn?
- Learned – What did I learn?
This three-step approach structures the reading experience into distinct phases: pre-reading, active reading, and post-reading reflection. It works especially well in reading comprehension, inquiry-based learning, and project-based environments.
Teachers and facilitators often use a KWL chart to visually guide this process and help learners organize their thoughts before, during, and after reading.
Why Use the KWL Strategy in Reading?
The KWL strategy turns passive reading into an active thinking process. Instead of jumping straight into a text, learners begin by engaging with what they already know. They then set learning goals and questions, which keep reading purposeful. At the end, they consolidate learning through structured reflection.
Benefits of the KWL method include:
- Encourages active reading and focused thinking
- Increases engagement and ownership of learning
- Improves retention through reflection
- Supports differentiated instruction and collaborative learning
- Works across subjects and formats (texts, videos, workshops)
How to Use the KWL Reading Strategy
Let’s break down each phase with actionable tips and examples.
Step 1: Know – Activating Prior Knowledge
Start by asking learners what they already know about the topic. This builds connections between existing knowledge and new information, making it easier to understand and retain what’s read.
What to include in the “Know” column:
- Key terms or concepts
- Facts, definitions, or examples
- Personal experiences
- Common assumptions or misconceptions
Step 2: Want to Know – Setting Learning Goals
In this stage, learners define what they want to know or what questions they hope the reading will answer. This sets a purpose and encourages inquiry.
How to craft better questions:
- Turn general curiosity into specific, open-ended questions
- Align questions with lesson objectives
- Group similar questions using tags or categories
- Encourage peer discussion to refine the question list
This step helps learners read with intention and gives educators a way to measure learning progress.
Step 3: Learned – Reflecting and Reviewing
After reading, students revisit their original questions and record what they’ve learned. This column also allows space to correct misconceptions, note surprising facts, and summarize key insights.
Tips for maximizing this step:
- Compare the “Learned” column with the “Want to Know” questions
- Reflect on any changes in understanding or beliefs
- Use insights as a basis for assessments or essays
- Encourage group reflection and peer feedback
KWL Chart Templates for Reading and Literacy Activities
Use these ready-to-edit KWL chart templates to engage learners in reading, vocabulary building, and subject-specific exploration. Perfect for classrooms, homework, or group projects.
English KWL Chart: Novel Study
Help students explore themes, characters, and plot elements in fiction with a structured KWL chart designed for literature analysis.
Vocabulary KWL Chart: Academic Word List
Boost word retention and context understanding by using this chart to track what students know and want to learn about academic vocabulary.
Reading Comprehension KWL Chart for Literature Class
Guide students through close reading and critical thinking by organizing their prior knowledge, learning goals, and takeaways from literary texts.
Middle School KWL Chart: Ancient Civilizations
Support history or social studies units with a focused KWL chart that prompts inquiry and reflection around major ancient cultures.
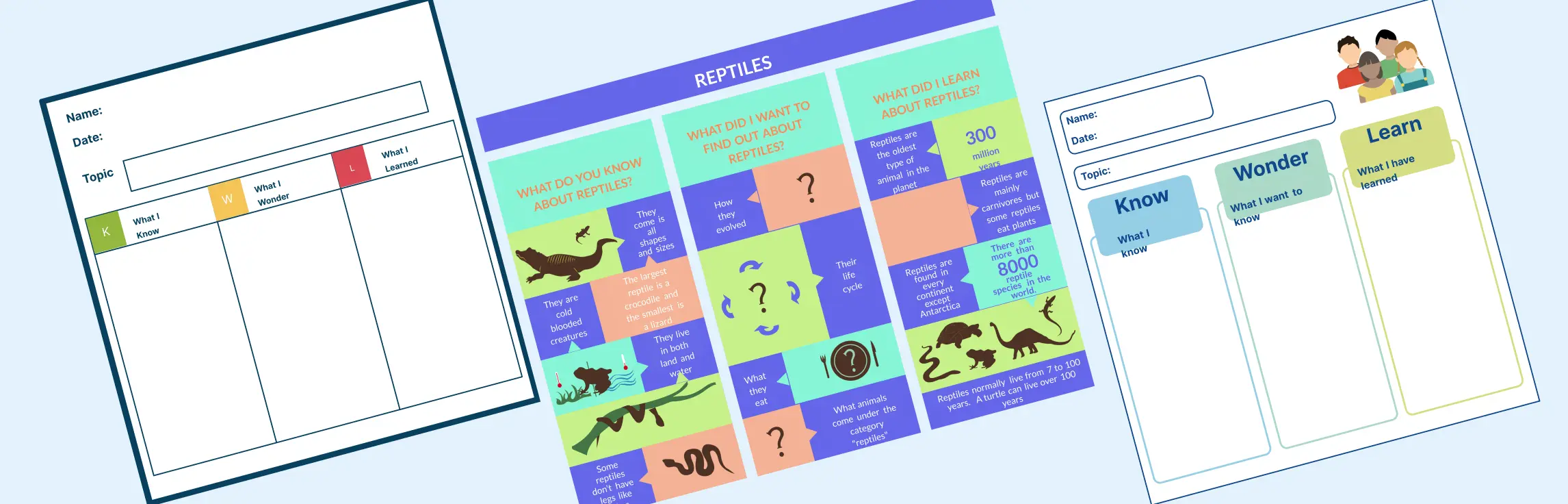
Science KWL Chart: Chemical Reactions
Encourage scientific thinking by using this chart to connect existing knowledge to new discoveries about chemical processes and reactions.
What to Watch Out for When Using the KWL Strategy for Reading
The KWL reading strategy is a powerful tool—but like any instructional method, it works best when applied thoughtfully. Here are a few practical considerations to help you get the most out of your KWL charts and ensure your students stay engaged and supported throughout the process.
1. Watch for Gaps in Background Knowledge
Some students, especially English as an Additional Language (EAL) learners, may not have enough context to confidently fill out the “Know” column. This doesn’t mean they lack prior knowledge—it may just mean the topic needs a stronger connection to their lived experience.
- Tip: Choose accessible texts and offer scaffolding when needed. Use visual cues, real-world examples, or pre-reading discussions to help students activate related knowledge, even if it’s not directly about the topic.
2. Provide Support with Vocabulary
Technical terms and unfamiliar abbreviations can make a text difficult to approach, especially during the “Want to Know” and “Learned” stages. If students encounter too many unknowns, they may disengage or feel overwhelmed.
- Tip: Pre-teach key vocabulary and provide glossaries or word banks alongside your KWL chart. This ensures students have the language tools they need to explore the topic confidently.
3. Guide Learners When They’re Stuck in the “K” Column
Sometimes students struggle to come up with what they “know”—or share misconceptions. This might happen if the topic feels too unfamiliar or if the question asked doesn’t connect with their real-world experiences.
- Tip: Reframe the prompt. Instead of asking “What do you know about ecosystems?” try, “What do you know about living things or nature?” Broaden the frame to activate prior knowledge that’s more relatable.
4. Manage Overly Broad or Limited “W” Questions
Younger students may generate too many unrelated questions in the “Want to Know” column, while older students may claim they have no questions at all.
- Tip: Try asking “What do you think you will learn?” This shifts the focus from curiosity to prediction, helping students engage their inferencing skills and build anticipation before reading.
5. Embrace Diverse Interpretations in the “L” Column
Learners may arrive at different takeaways based on personal experiences or cultural perspectives. It’s important to honor those insights, even if they differ from the intended meaning of the text.
- Tip: Facilitate open discussions. Encourage students to share how their understanding aligns with or diverges from the text. Reinforce the idea that while personal responses matter, comprehension must come first before critique.
This thoughtful approach helps ensure your KWL strategy works as intended; building confidence, enhancing comprehension, and encouraging critical thinking in every learning environment.
Helpful Resources
Explore the purpose, key benefits, and how to use KWL Charts effectively with ready-to-use templates. Boost learning through structured inquiry.
Discover how the KWL strategy boosts learning, reading, and test prep. Includes chart examples, visual templates, and tips for effective implementation.
Explore 15 KWL chart examples for preschool to high school, corporate training, and subject-specific learning.
Explore the top KWL benefits for learners. Learn how KWL charts promote reflection, engagement, and goal-setting. Includes templates for easy classroom use.
KWL Strategy in Action: Real-World Examples
The KWL strategy in reading isn’t limited to textbooks. It adapts well to diverse learning scenarios such as:
- Classroom reading: Use KWL charts for novels, science chapters, or history topics.
- Workshops: Prepare learners for professional development topics like leadership or communication.
- Documentary viewings: Capture key points before and after watching.
- Corporate training: Align team objectives and knowledge-sharing in onboarding or product training sessions.
- Project research: Use KWL as a scaffold for inquiry-based or cross-disciplinary research tasks.
You can even extend the framework to KWHL by adding a fourth column: H – How will I learn this?
The KWL reading strategy transforms reading into a purposeful learning journey. It’s simple to implement, easy to adapt, and highly effective across all ages and learning environments. By pairing it with visual tools like Creately, educators can enhance collaboration, guide deeper inquiry, and make reflection a natural part of the reading process.
Whether you’re working with young learners, teenagers, or adult professionals, KWL charts provide a consistent structure for guiding and measuring learning.
Resources:
Husnaini, H. (2018). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF KNOW –WANT-LEARN (KWL) STRATEGY IN TEACHING READING COMPREHENSION. IDEAS: Journal on English Language Teaching and Learning, Linguistics and Literature, 6(2). doi:https://doi.org/10.24256/ideas.v6i2.512.
Jstor.org. (2024). K-W-L Plus: A Strategy for Comprehension and Summarization on JSTOR. [online] Available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/40031872.
Usman, B., Fata, I.A. and Pratiwi, R. (2019). TEACHING READING THROUGH KNOW-WANT-LEARNED (KWL) STRATEGY: The effects and benefits. Englisia Journal, 6(1), p.35. doi:https://doi.org/10.22373/ej.v6i1.3607.
FAQs About KWL Reading Strategy
What is a KWL chart?
A KWL chart is a three-column graphic organizer used to guide learning before, during, and after reading or research. The columns stand for:
- K – What I Know
- W – What I Want to Know
- L – What I Learned
KWL charts help students activate prior knowledge, set purposeful learning goals, and reflect on new information. They’re widely used in classrooms to improve reading comprehension, foster curiosity, and support metacognitive thinking.