Choosing between Gantt chart vs Kanban isn’t just about picking a visual—it’s about how your team thinks, plans, and delivers. Some projects thrive on timelines, milestones, and clear sequences, while others need flexibility, flow, and quick adaptability. In this guide, we’ll explore where each approach shines, how they influence collaboration, and real scenarios to help you decide which style fits your work (or when combining both is the real game-changer).
What Is a Gantt Chart?
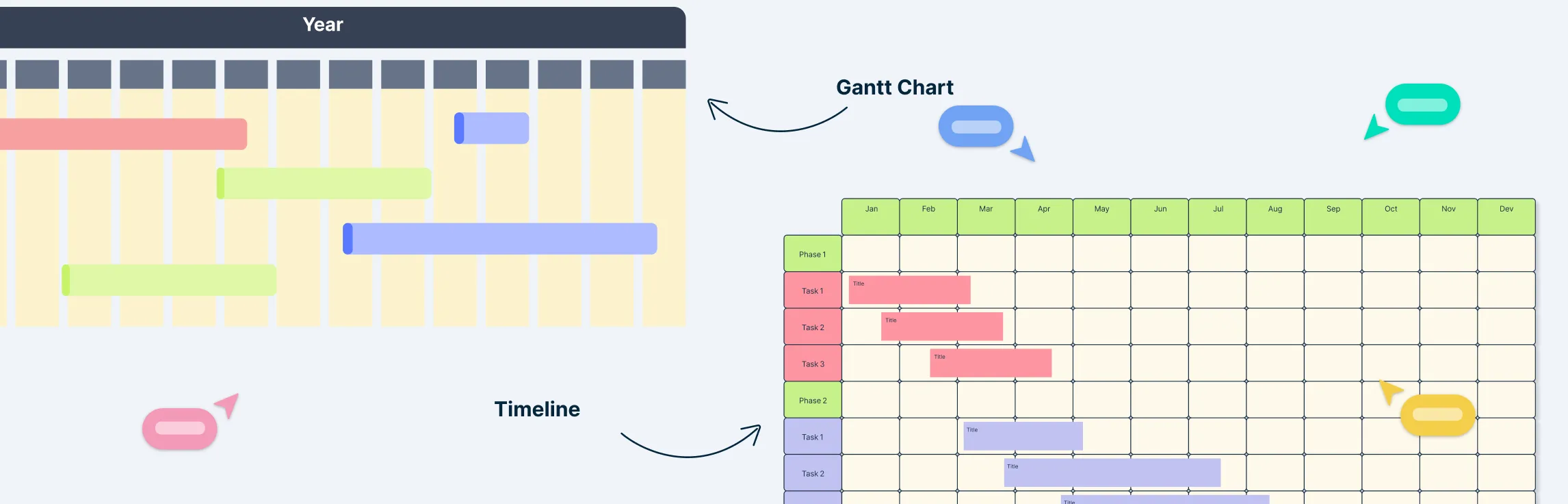
A Gantt chart is a visual project planning tool that displays tasks on a timeline. Each task is represented as a horizontal bar, showing when work starts, how long it lasts, and when it is expected to be completed. It helps teams see the big picture—who is doing what, when tasks overlap, and how changes affect the overall schedule. Gantt charts are especially useful when projects have deadlines, dependencies, or milestones that must be tracked and coordinated across teams.
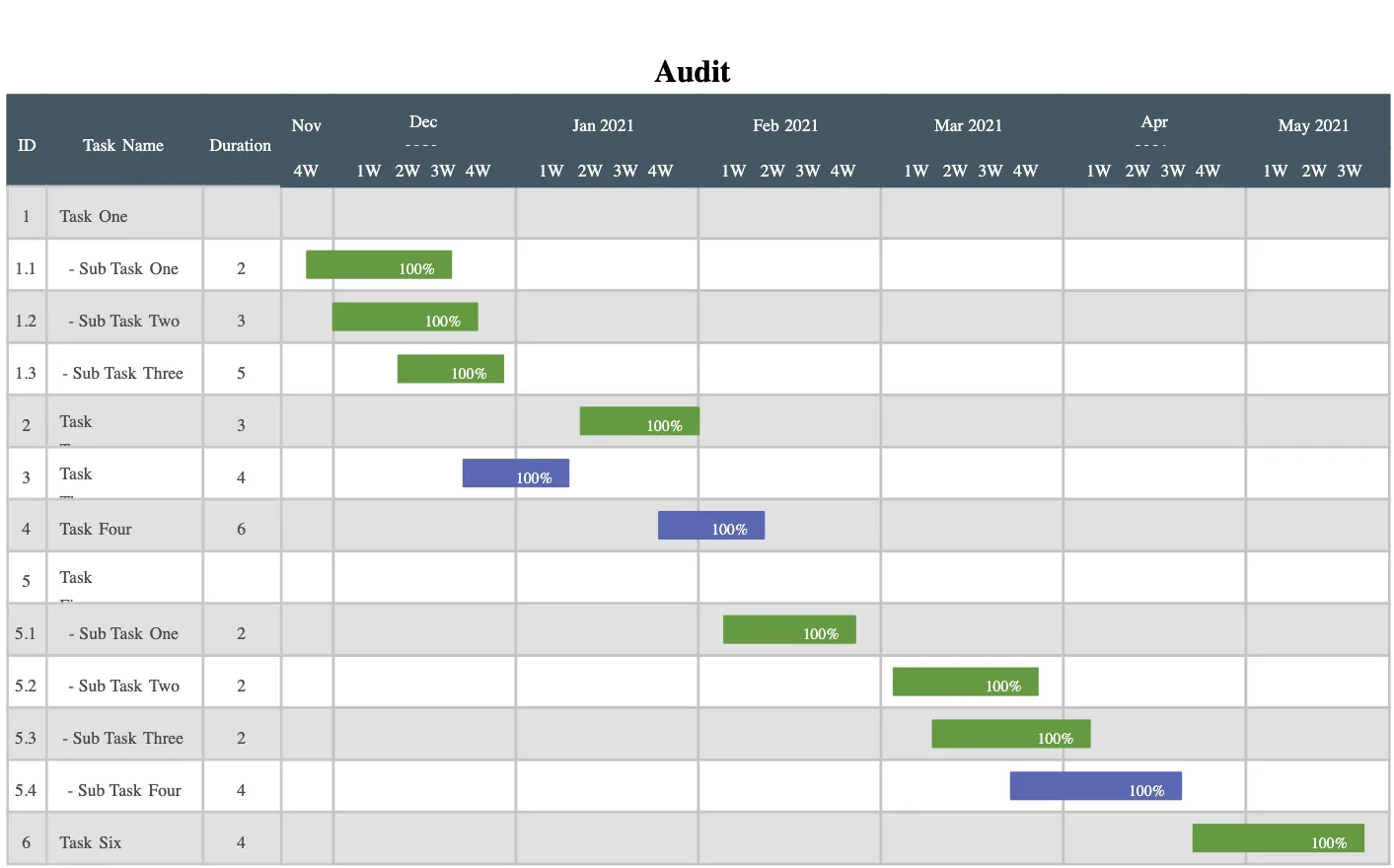
Key components of a Gantt chart
Tasks (activities or work items): Individual pieces of work that need to be completed. These form the basis of the chart.
Timeline: The horizontal axis, typically broken down by days, weeks, or months, depending on project length.
Task bars: Horizontal bars representing the duration of each task. The bar’s start and end correspond to planned start and finish dates.
Dependencies: Relationships between tasks (e.g., Task B can’t start until Task A finishes). They’re usually shown with arrows linking tasks.
Milestones: Zero-duration markers for important deadlines, deliverables, or project checkpoints (e.g., beta release, launch).
Assignees or owners: Indicate who is responsible for a task. Some charts display these next to the bar or in a separate column.
Progress indicators: Often a shaded or filled portion of the task bar showing how much work has been completed.
What Is a Kanban Board?
A Kanban board is a visual workflow management tool that helps teams track and optimize the flow of work. Tasks are represented as cards and move across columns that reflect different stages of a process, making it easy to see what’s in progress, what’s pending, and what’s done. Kanban emphasizes limiting work-in-progress (WIP), reducing bottlenecks, and improving efficiency. Kanban boards are widely used in agile teams, service operations, and any environment where work flows continuously rather than in fixed phases.
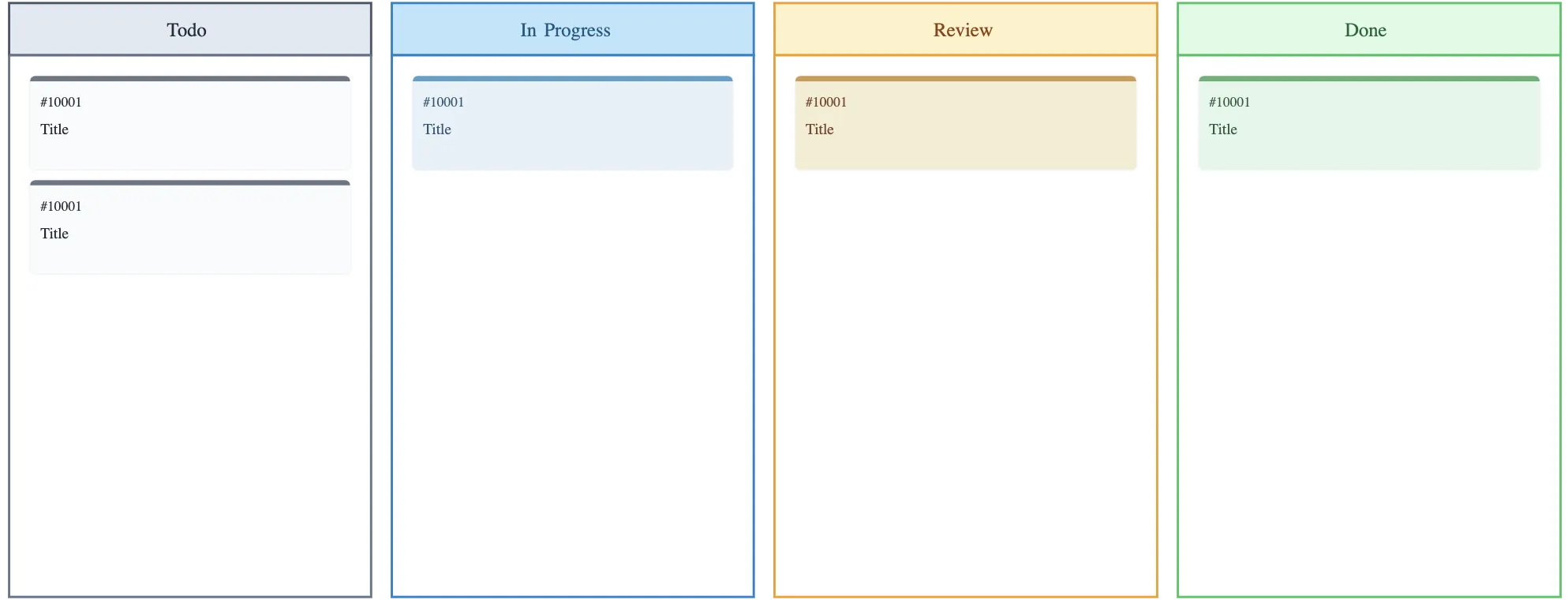
Key components of a Kanban board
Columns: Represent stages of the workflow (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done). They show where each task is in the process.
Cards: Individual tasks or work items. Each card contains details such as task description, assignee, due date, and priority.
Work-in-progress (WIP) limits: A maximum number of tasks allowed in a column at one time to prevent overloading the team and ensure smooth flow.
Swimlanes: Optional horizontal lanes that group tasks by type, team, priority, or project, adding extra organization.
Task details / metadata: Includes assignee, due dates, labels, checklists, attachments, or tags to provide context for each task.
Visual indicators: Flags, color-coding, or icons highlight blockers, priorities, or deadlines to make the board easy to scan at a glance.
Gantt Chart vs. Kanban Board: Key Differences
| Feature | Gantt Chart | Kanban Board |
| Purpose | Visualizes project schedule, task durations, and dependencies | Visualizes workflow, tracks task progress, and optimizes flow |
| Focus | Timeline-oriented; planning and sequencing of tasks | Flow-oriented; continuous movement of work through stages |
| Visual Layout | Horizontal bars on a timeline | Columns representing workflow stages, with tasks as cards |
| Planning Horizon | Long-term planning; fixed start and end dates | Short-term and ongoing; flexible, continuous work |
| Dependencies | Strongly shows task dependencies and critical path | Dependencies are implicit or visualized with swimlanes or blockers |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; changes require updates across the timeline | Highly flexible; tasks can be reprioritized or moved easily |
| Best For | Projects with clear deadlines, milestones, and complex task sequences | Continuous delivery, support work, agile teams, and operations |
| Progress Tracking | Tracks progress by completion percentage of task bars | Tracks flow visually as cards move across columns |
| Workload Management | Indirect; workload inferred from task durations | Direct; WIP limits prevent overloading team members |
| Ease of Update | Can be time-consuming for large projects | Easy to update in real-time |
| Team Collaboration | Useful for overview; less interactive | Highly collaborative; team can pull tasks and communicate on cards |
Similarities Between Gantt Charts and Kanban Boards
Even though Gantt charts and Kanban boards look very different, they share the same core purpose: making work easier to manage through visibility and structure. Both tools help teams understand what needs to be done, who’s doing it, and how projects are progressing—without digging through emails or spreadsheets.
Both are visual project management tools, turning work into something you can see and interact with.
They increase task visibility, helping teams understand current work, upcoming items, and completed tasks.
Each supports collaboration, giving everyone a shared source of truth instead of scattered information.
They enable progress tracking, making it easy to spot delays, blockers, or stalled tasks.
Both encourage transparency and accountability, ensuring responsibilities and deadlines are clear.
They scale well—from simple personal task management to complex multi-phase projects.
When to Use a Kanban Board vs Gantt Chart
When to use Gantt charts
Gantt charts are ideal when your project needs clear timelines, structured sequences, and careful tracking of dependencies. Create a Kanban board when:
Your project has fixed deadlines or milestones.
Tasks are dependent on one another and delays could impact the overall schedule.
You need a big-picture overview for stakeholders or management.
Planning resource allocation across multiple teams or phases.
You want to track progress against a schedule and identify bottlenecks in advance.
Examples: product launches, construction projects, marketing campaigns with launch dates, regulatory compliance projects.
When to use Kanban boards
Kanban boards work best for teams that handle continuous flow of work, need flexibility, or want to visualize current workload. Create a Gantt chart when:
Work is ongoing and not tied to strict deadlines.
You need real-time visibility into task progress.
Frequent changes in priority are expected.
You want to limit work-in-progress and avoid team overload.
Collaboration and quick updates are important.
Examples: support/helpdesk teams, software maintenance, content creation pipelines, agile development sprints, operational workflows.
Getting the Best of Both Worlds: Combining Gantt and Kanban
You don’t have to pick “Gantt or Kanban” — the real magic happens when you use both together. A smart hybrid setup gives you the high-level structure of a Gantt chart and the daily team flow of a Kanban board. Here’s how to do it right.
Why combine Gantt and Kanban?
Strategic planning + flexible execution: Use a Gantt chart to map out project phases, milestones, and dependencies. Then switch to Kanban for the day-to-day work where tasks move in real time.
One source of truth: Modern hybrid tools can sync both views so updates in your Kanban board reflect on your Gantt chart, and vice versa — no double‑handling.
Better visibility for different stakeholders: Leaders can review the big picture in Gantt, while teams stay grounded in Kanban for what’s immediately next.
Bottleneck detection: You can compare Kanban flow issues (like stalled cards) with Gantt timeline delays to spot and resolve problems earlier.
Smart ways to combine them
Plan with Gantt, execute with Kanban: Map out project phases, milestones, and dependencies on a Gantt chart template, then break them into actionable tasks on a Kanban board for daily execution.
Link milestones to Kanban tasks: Connect Gantt milestones to Kanban cards so your workflow stays flexible while keeping deadlines visible.
Visualize dependencies and flow together: Use Creately to display task dependencies in Gantt while tracking progress and WIP on your Kanban board for real-time clarity.
Monitor progress and spot bottlenecks: Compare task timelines with Kanban flow to quickly identify stalled work or potential schedule delays.
Iterate and adjust easily: As priorities shift, update tasks in Kanban; Gantt timelines automatically reflect progress, keeping your project on track without extra work.
Things to watch out for (pitfalls & best practices)
Avoid rigid Gantt over-detail: Don’t let your timeline force unrealistic deadlines or micro-manage daily work. Use Gantt for planning, not constant control.
Keep data consistent: Use a tool that supports real-time syncing — otherwise, you’ll end up duplicating effort or working with out-of-date views.
Train your team: Some may prefer Kanban, others Gantt. Make sure everyone knows when to use each view and how to interpret them.
Use hierarchical task breakdowns: Map big phases in Gantt, then break them into smaller work items on Kanban with defined dependencies.
Helpful Resources
Professionally designed Gantt chart templates available in the Creately diagramming community.
Learn how to use Gantt charts to plan projects, why they are useful and how to effectively use them in a project.
Explore Kanban vs Scrum in this ultimate guide. Learn key differences, benefits, use cases, and how to choose the right agile framework for your team’s workflow.
Free Kanban and Gantt Chart Templates
Now that you know the difference between a Gantt chart and a Kanban board and how to use them, here are some templates to get you started.
Gantt chart templates
Ready-to-Use Gantt Chart Template
Colored Gantt Chart Example
Hotel Management System - Gantt Chart
Gantt Chart for Business plan
Kanban board templates
AI Kanban Board Template
Kanban Card Template
IT Kanban Board
Software Kanban Board
It depends on the work style: You can use Creately to create both Gantt charts and Kanban boards seamlessly in one platform. Creately offers a range of features designed to make project planning and workflow management simple and visual:FAQs About Gantt Chart vs Kanban Board
Are Gantt charts or Kanban boards better for long-term planning?
Which is better for small teams?
Is Kanban only for software or agile teams?
How do I show task dependencies in Kanban?
Can Gantt charts and Kanban help improve team collaboration?
What tool can I use to create a Gantt chart and Kanban board?