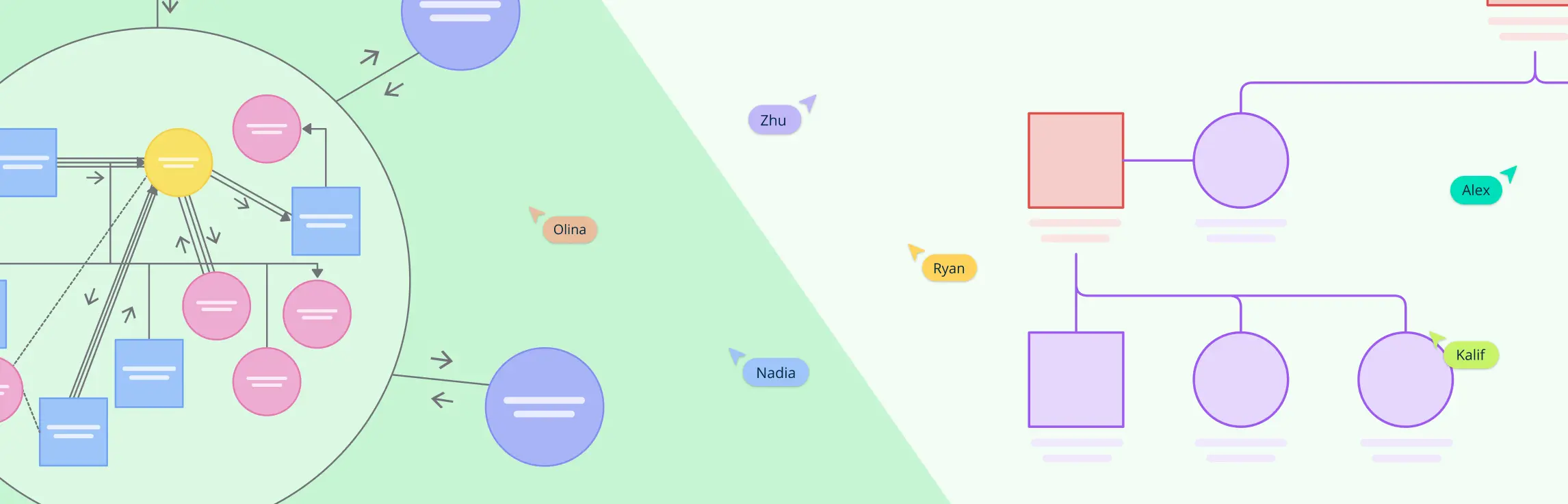
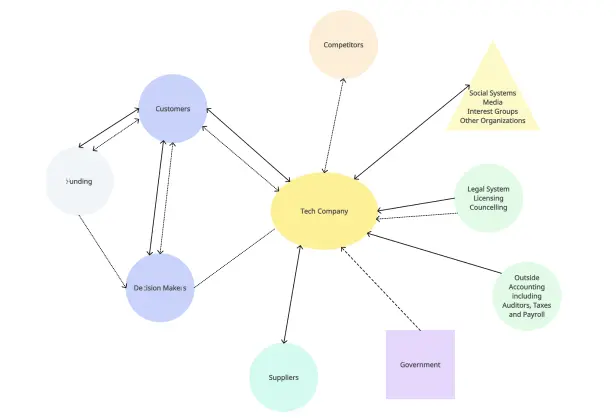
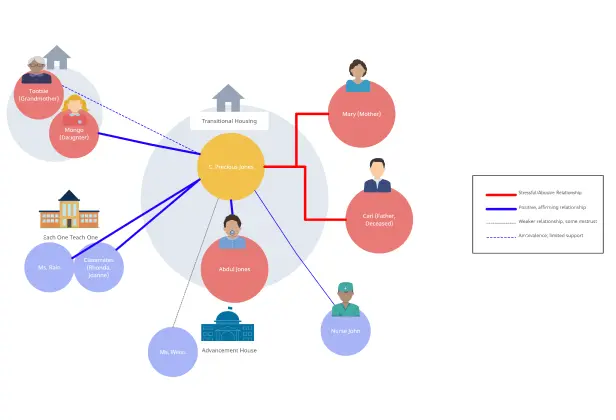
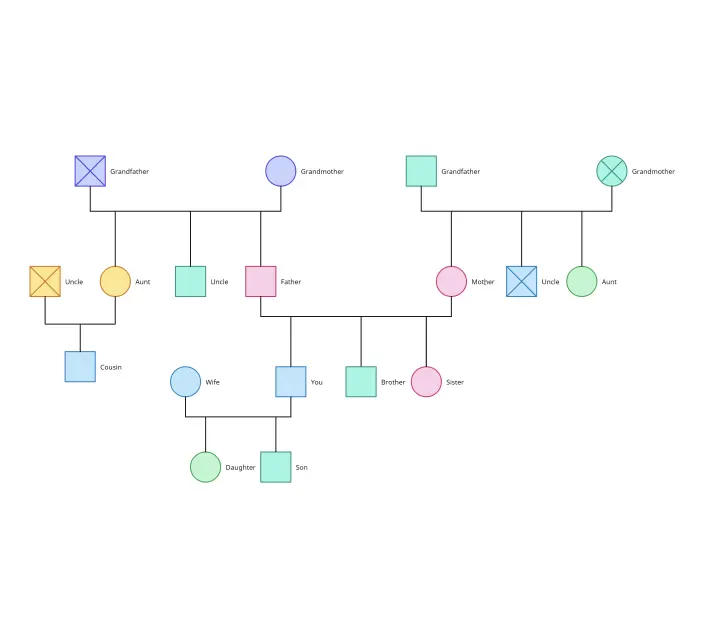
Understanding relationships, whether within a family or between an individual and their social environment, is key to gaining valuable insights. This is where tools like genograms and ecomaps come in.
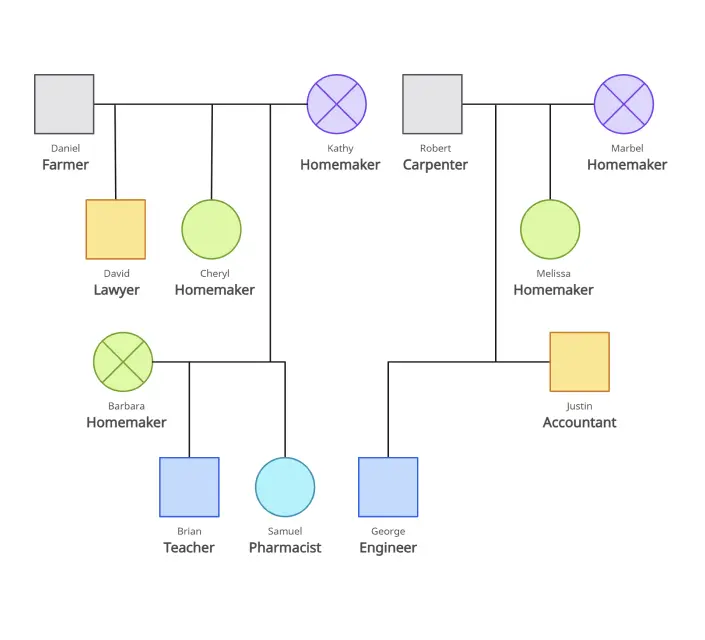
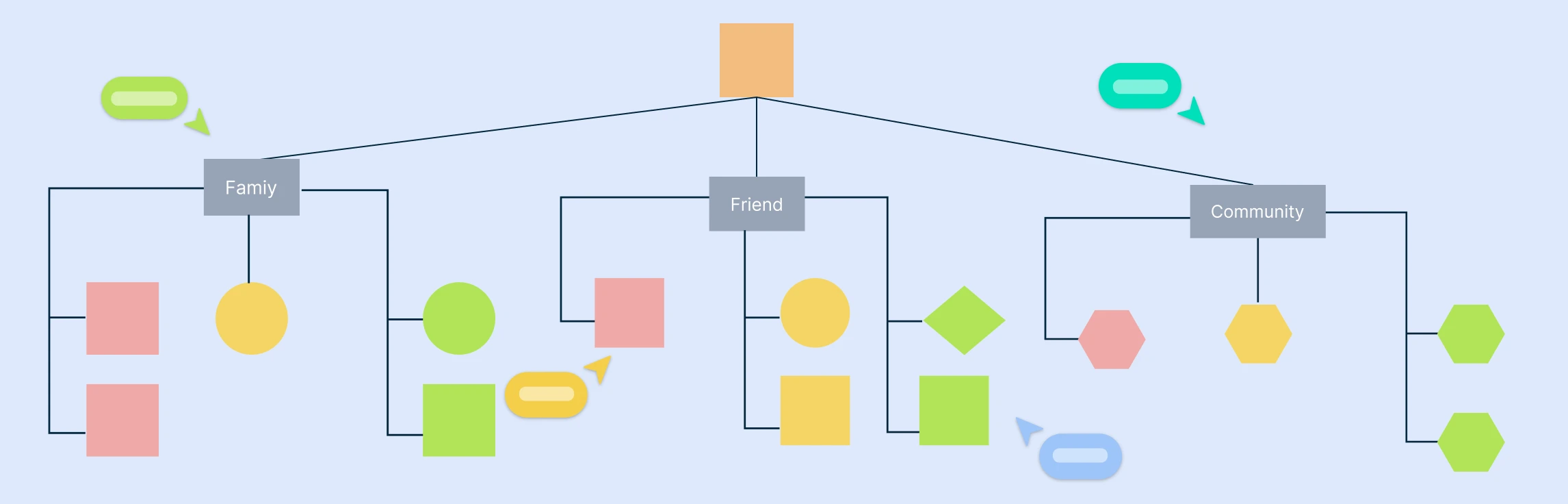
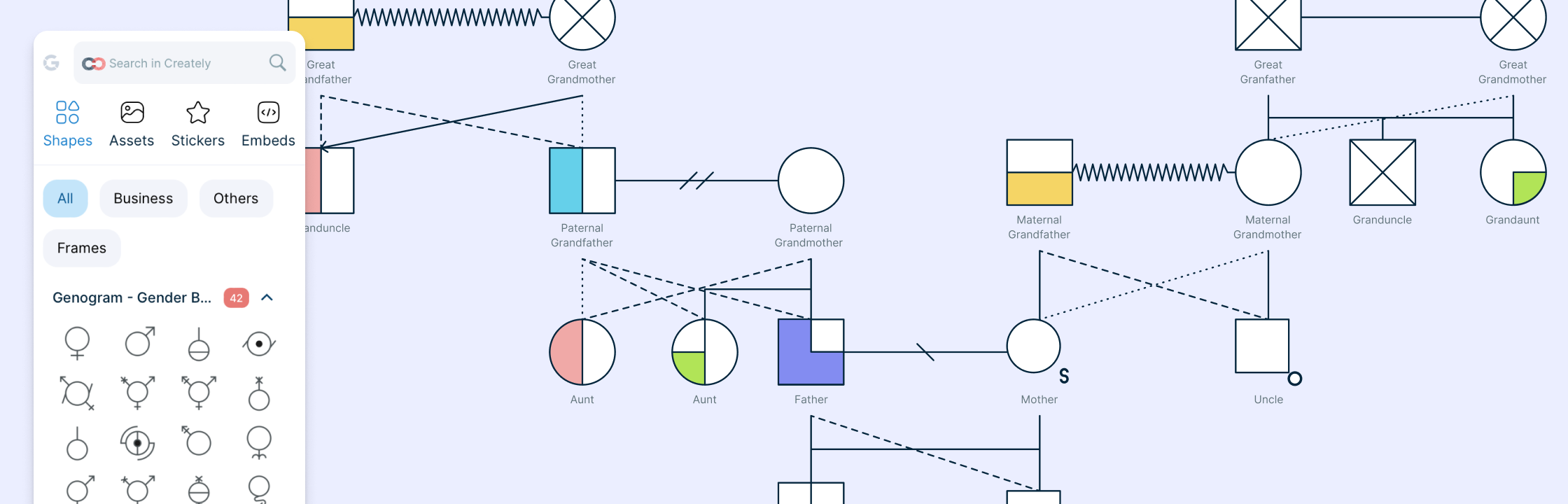
A genogram helps you dive deep into family structures and dynamics, showing patterns that span generations. On the other hand, an ecomap looks outward, mapping the connections between a person or family and the world around them, such as friends, workplaces, or community resources.
Genogram VS Ecomap
| What is a Genogram | What is an Ecomap |
|---|---|
| A genogram is like a detailed family tree that goes beyond names and dates. It visually maps out who is in the family, how they are connected, and recurring patterns. | An ecomap is a visual tool that maps a person’s relationships with people, groups, and organizations in their external environment, highlighting support or stress factors. |
| Purpose of a Genogram | Purpose of an Ecomap |
|---|---|
| To understand family dynamics and spot trends such as hereditary health conditions, emotional ties, or recurring issues across generations. | To understand someone’s support system by identifying where help comes from, the strength of connections, and areas needing more resources. |
| Key Elements of a Genogram | Key Elements of an Ecomap |
|---|---|
| • Family relationships: Shows marital status, divorces, parent-child links, etc. | • Social networks: People and groups in the person’s life (family, friends, coworkers). |
| • Hereditary patterns: Tracks health conditions or traits passed down generations. | • Resource mapping: Shows resources like schools, healthcare, support groups. |
| • Emotional dynamics: Illustrates emotional quality of relationships like closeness or conflict. | • External systems: Connects to institutions (e.g., workplaces, government) and indicates relationship quality. |
| Common Use Cases | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|
| • Therapy: Understanding family dynamics for client insights. | • Social Work: Assessing support networks and identifying needs. |
| • Healthcare: Tracking hereditary conditions for diagnosis or prevention. | • Counseling: Exploring influences and stressors in someone’s life. |
| • Genealogy: Visualizing and organizing family history. | • Support System Analysis: Finding gaps and strengthening external relationships. |
Key Differences Between Ecomap and Genogram
| Comparison Area | Genogram | Ecomap |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Focuses on family relationships and history. Acts like a deep family tree showing emotional dynamics, hereditary patterns, and generational links. | Focuses on external social connections. Maps relationships with people, groups, and institutions like friends, schools, and workplaces. |
| Purpose | Helps understand where someone comes from by uncovering patterns and exploring family influences on their life. | Helps understand how someone interacts with the world by analyzing support systems and identifying social or resource gaps. |
| Components | Includes family members and their relationships. Uses symbols and lines to show emotional closeness, health conditions, and structural dynamics. | Includes the individual/family at the center with lines connecting to external systems (positive, neutral, or stressful relationships). |
| Applications | Common in therapy, healthcare, and genealogy to track hereditary traits, family history, and relationship patterns. | Used in social work, counseling, and support planning to assess external environments and strengthen support networks. |
| Timeframe | Looks to the past to uncover generational trends and historical patterns that shape a person’s present. | Looks at the present to identify current supports, stressors, and actionable needs in a person’s external life. |
Similarities Between Genogram and Ecomap
Genograms and ecomaps are alike in their ability to visually map relationships, uncover patterns, and provide meaningful insights.
1. Both are visual tools
Instead of relying on long descriptions, these tools let you quickly grasp someone’s family structure or social network.
- Genograms and ecomaps use symbols, lines, and shapes to represent relationships and connections, making it easy to see patterns at a glance.
- They turn complex information into a simple, clear visual that’s easy to understand and analyze.
2. Both help identify patterns
Both tools reveal underlying trends that can guide problem-solving and decision-making.
- A genogram identifies family-related patterns, like hereditary health issues or recurring emotional conflicts.
- An ecomap identifies social patterns, like strong support systems or areas where someone feels isolated.
3. Both are used for better understanding
Both tools help build a fuller picture of someone’s life, which is essential for offering effective support or solutions.
- They aim to help professionals like therapists, counselors, and social workers gain deeper insights into a person’s life.
- Genograms provide context about someone’s family, while ecomaps provide context about their social and external environment.
4. Both highlight relationships
Both tools show the strength or weakness of relationships, helping identify areas of support or conflict.
- A genogram focuses on family relationships—who’s connected to whom and the quality of those connections.
- An ecomap focuses on social relationships, like connections to friends, workplaces, and community resources.
5. Both are interactive and flexible
This flexibility ensures both tools can adapt to the person’s unique needs and story.
- You can add, update, or customize details on both genograms and ecomaps to suit the situation.
- For example, you can highlight a specific issue, like a family health condition on a genogram or a stressful relationship with an employer on an ecomap.
When to Use Genogram and Ecomap
Genograms and ecomaps are useful in different situations, depending on what you want to understand about a person’s life. Here’s when to use each:
| When to Use Genograms | When to Use Ecomaps |
|---|---|
| Use a genogram when you want to focus on family dynamics and history. It’s great for understanding: | Use an ecomap when you need to look at a person’s social and external environment. It’s helpful for: |
| • Family patterns: Like hereditary health issues, recurring behaviors, or family traditions. | • Assessing support systems: To see who or what provides help, like friends, workplaces, or community services. |
| • Emotional relationships: To see if there’s conflict, closeness, or other dynamics between family members. | • Identifying stressors: To find out which connections are causing stress or difficulties. |
| • Generational connections: To explore how family roles and relationships have evolved over time. | • Resource planning: To identify gaps in their access to support, like a lack of childcare or transportation. |
How to Use Genograms and Ecomaps Together
Genograms and ecomaps are powerful tools on their own, but combining them can give you an even deeper understanding of someone’s life. While a genogram focuses on family relationships and internal dynamics, an ecomap shows how a person connects with the world outside their family. Together, they provide a full picture of both internal and external influences.
Free Genogram and Ecomap Templates
You might combine these tools when you want to explore how family patterns and relationships interact with someone’s external support system. For example: A therapist might use both to understand how family conflicts impact a person’s ability to rely on friends or community resources. A social worker could look at how a person’s family history affects their access to or use of external support systems like healthcare or housing services.FAQs About Genogram and Ecomap
Are genograms and ecomaps only used in therapy?
How do I represent conflicts in a genogram?
Can an ecomap show a person’s career network?
How detailed can an ecomap get?
How can a genogram be used in genealogy research?
How do I use a genogram and ecomap to improve social support?
When to combine genograms and ecomaps